OPINION
Uganda first discovered oil in 2006, marking a significant milestone in the nation’s economic aspirations. By 2010, interest in exploration and extraction intensified, with oil companies and development partners making substantial investments. Projects such as Tilenga, Kingfisher, and the East African Crude Oil Pipeline (EACOP) have since been launched, promising to drive economic growth. However, global and local experiences warn of potential risks associated with heavy dependence on fossil fuels, including economic volatility, environmental degradation, social disruption, and difficulties in adapting to cleaner energy sources.
Many Ugandans initially believed that the oil boom would transition the country to middle-income status, prioritizing people over profits. Instead, it has brought distress, displacement, and exploitation. Compensation for compulsory land acquisition has been inadequate, leaving communities, especially marginalized groups such as women, the elderly, and the youth,struggling against injustices that persist to this day.
The land acquisition process has triggered displacement, food insecurity, income inequalities, and violations of environmental and land rights. Many rural communities, traditionally reliant on agriculture, fishing, and farming, have been separated from their ancestral livelihoods. Additionally, oil extraction has led to deforestation, oil spills, and carbon emissions, exacerbating climate change and degrading the environment.
While the government touts job creation in the oil sector, it remains clear that employment opportunities have not benefited the general population, particularly in rural areas where oil is being drilled. The oil industry is highly capital-intensive, requiring advanced technology and specialized skills, resources that marginalized communities often lack. Furthermore, financial institutions, including banks such as KCB Uganda, Stanbic, and EXIM, continue to invest in fossil fuel projects like EACOP and Kingfisher, further entrenching dependence on oil.
The Case for Agriculture
Agriculture, in contrast, is the backbone of Uganda’s economy, employing over 90% of the population. It provides opportunities for both skilled and unskilled labor, particularly among marginalized communities who face systemic oppression. Before the discovery of oil, Ugandan communities thrived in harmony with the environment, engaging in sustainable agricultural practices that supported livelihoods and food security.
Agriculture is a viable green economic alternative that directly enhances climate resilience, livelihoods, and socio-economic development. As the world grapples with climate change, marginalized women and youth bear the brunt of its impact, underscoring the urgent need for investment in sustainable, regenerative economies.
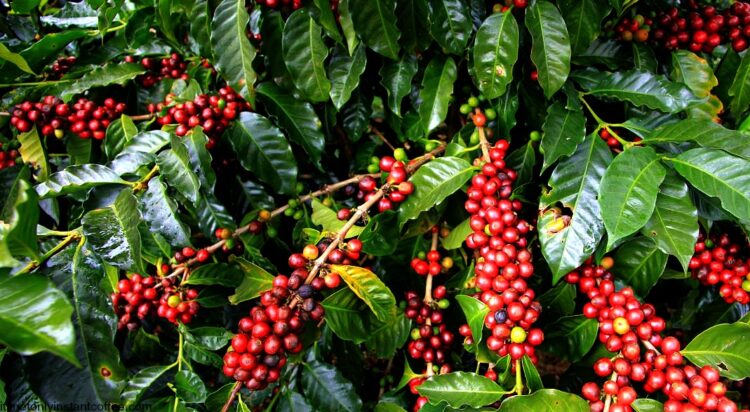
The agricultural sector, particularly coffee farming, sustains over 1.7 million households and 3.5 million individuals, with more than 90% being small-scale farmers value chain, from farmers to exporters, processors, baristas, and traders, ensuring widespread participation and fostering inclusive economic growth. By contrast, the oil sector concentrates wealth among a few stakeholders, leaving the majority of Ugandans excluded.
Moreover, agriculture is inherently sustainable. It prevents soil erosion, promotes carbon sequestration, and can be integrated into agroforestry systems that enhance biodiversity. Smart agricultural practices reduce global warming and mitigate climate change, strengthening resilience over time.
Despite existing challenges, farmers remain community-centered and adaptable, quickly implementing nature-based and locally led solutions to improve their livelihoods and create employment opportunities, particularly for youth.
The Path Forward
Given these realities, financial institutions, government leaders, and development partners must stop funding new fossil fuel projects and instead prioritize investments in green economic alternatives. Sustainable agriculture offers a just, equitable, and flexible economic model that benefits marginalized communities while preserving Uganda’s environment for future generations.
Uganda’s future should be built on regenerative economies that empower its people not exploit them.
Writer is: Ireen Twongirwe
Co-founder and Executive Director, Women for Green Economy Movement Uganda (WoGEMUganda)